Introduction
Work breakdown structure in project management refers to the breakdown of work into parts, but it doesn’t actually involve breaking down work; rather, breaking down deliverables. Breakdown structures are used widely in project management. It lets you plan, manage, and evaluate large projects. Project management is a big game in all industries, and poor project management is a big reason for project failure.
A good project plan, when boiled down to a work breakdown structure, provides the following:
- A roadmap for the team
- Project timescale
- The requirements
- Validation of the estimated cost
- Identifying any obstacles
- Sign of expected problems
What is a work breakdown structure?
Work breakdown structure (WBS) is a method that splits a project down into a hierarchy of deliverables, tasks, and subtasks.
Here’s what PMBOK says about the work breakdown structure:
“A deliverable-oriented hierarchical decomposition of the work to be executed by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables.”
All-in-all — “A work breakdown structure defines all the things a project needs to accomplish, organize into multiple levels, and display graphically.”
It defines the “what” of the project. Let’s have a look at a work breakdown structure example of a project divided into smaller, more manageable components.
Project title: Seminar
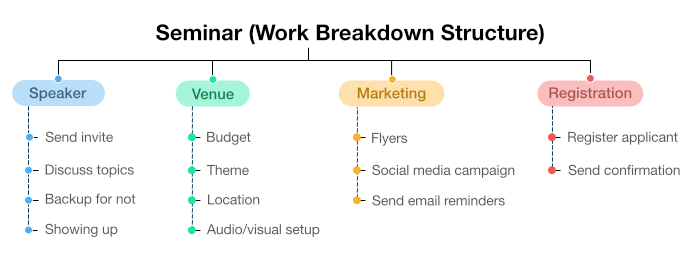
SA well managed WBS aids in scheduling, estimating costs, and determining risk. WBS helps eliminate unnecessary work to get the required results. The deliverable can be an object, a service, or an activity. It’s a simple yet methodical way of organizing your project scope into smaller, manageable components.
Ensure that poor project management doesn’t hinder your success. Try ProofHub now!
The must-know parameters of a work breakdown structure
The work breakdown structure in project management includes the part of project planning that people mostly oversee. It includes certain steps and rules that enable the project to run its course effectively and also help the team get a hang on things in a much more efficient way. Therefore, there are certain parameters to this process that one must know before starting to map out a breakdown structure and execute it to perfection. Some of these parameters are:
- Finding which individual is responsible for each piece of work
- The start and end dates
- Required resources
- Estimated cost of the project
- Requirements and milestones
- Protocol for quality control
How to create a work breakdown structure
In a project, planning and doing is an important part. And creating a WBS is where both are met. It is like making a flowchart that breaks all of the deliverables down into the tasks that need to be done to tick off the project. The visualization of the tasks in the WBS makes sure you’re accounting for every task as you plan your project out.
To understand how to create a work breakdown structure in a better way, here are the steps that everyone should understand:
1. Gather and document all intel:
Collect crucial project-related information like the requirements, code of conduct, list of deliverables, and the larger goals and milestones.
2. Make a definitive list of human resources:
To make sure to deliver an efficient product on time, you need to have a handful of people by your side who are up to the task. The most brilliant way to do that would be to judge what your project needs, match those kinds of tasks with the required skills and choose your project team wisely.
3. Come up with a defined set of deliverables:
It is always wise to set down a list of deliverable items and collaborate those with the expectations of the clients, the status of your resources, and the pace of your team. Therefore, try to capture the scope of your project in the best way that you can and determine what to deliver and when. These deliverable products/feature sets will be your Level 1 elements that will be catered to in the work breakdown structure in accordance with the 100% Rule.
4. Break everything down to units
As the words work breakdown structure suggests, this step will allow you to break all the Level 1 deliverables into unique smaller deliverable items. All you need to do for this process is map out the path to reach these unique deliverables through a sequence of tasks. Keep on breaking all the processes as well as the tasks until all you have are these doable actions that are performed by an individual or a select group of people. All these doable actions will be known as the Work Packages.
5. Map every task and dependencies with Gantt charts
Gantt charts are the perfect tools for visualizing tasks, scheduling activities, and managing project dependencies. Therefore, when you are done mapping out what to do and the sequence you want to attempt all your tasks, use Gantt chart software to schedule and visualize all your tasks, assign people to these tasks, and set appropriate deadlines for the same.
Levels of a work breakdown structure
The levels of a Work Breakdown Structure are branched hierarchically. A WBS mainly has four levels as a hierarchy, but it can have more depending on the project’s complexity and scale.
- The Top Level: Project Title
The project title and final deliverables are listed at the top level of a WBS. You can begin developing your WBS in this part by defining the project’s overall scope. Use simple language to describe what the finished project should look like so that everyone on your team knows what they’re aiming for. A WBS’s top level might be a useful means of communicating your client’s needs for the finished project.
- Control Accounts
Control Accounts is the second of the WBS Levels. Control accounts are significant project components, systems, phases, or deliverables. The primary phases of a project and the essential deliverables that must be met are outlined at the controlling account level. It can also refer to the components and features that must be included in the end project to suit the customer’s requirements.
- Work Packages
Under the controls account level, a WBS’s work packages level exists. The main deliverables are broken down into smaller, more doable activities at this level. Teams must first complete the tasks outlined in the work packages level to succeed at the controls account level.
- Activities
The activities level is the final WBS level. The tasks that must be allocated to project team members to fulfill the work package are known as activities. This level contains all of the tasks that must be performed before a team may begin working on the work packages.
Key elements of work breakdown structure
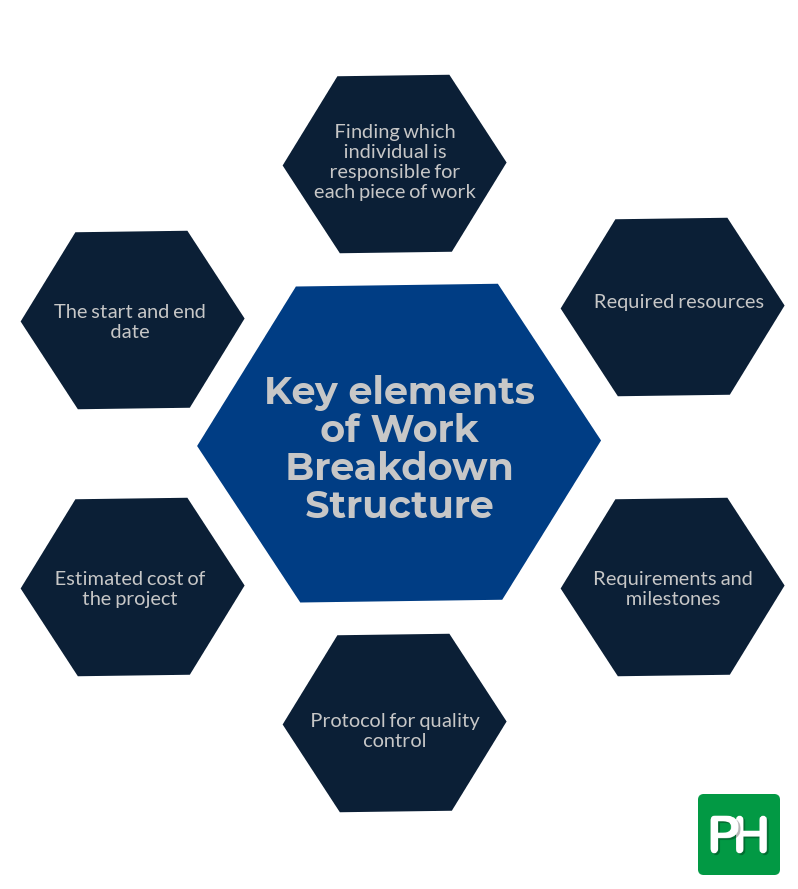
- Finding which individual is responsible for each piece of work
- The start and end dates
- Required resources
- Estimated cost of the project
- Requirements and milestones
- Protocol for quality control
Examples of a work breakdown structure
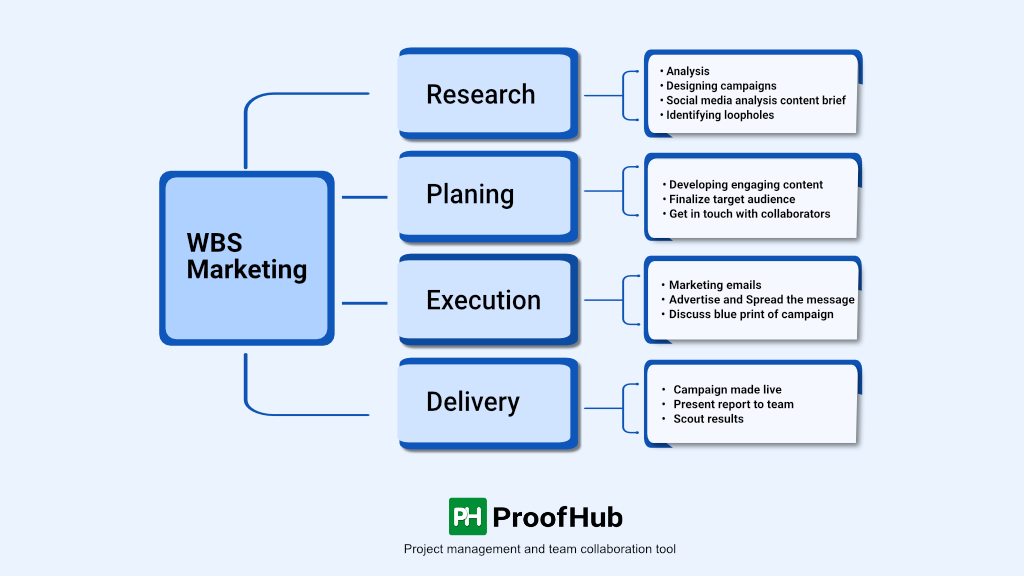
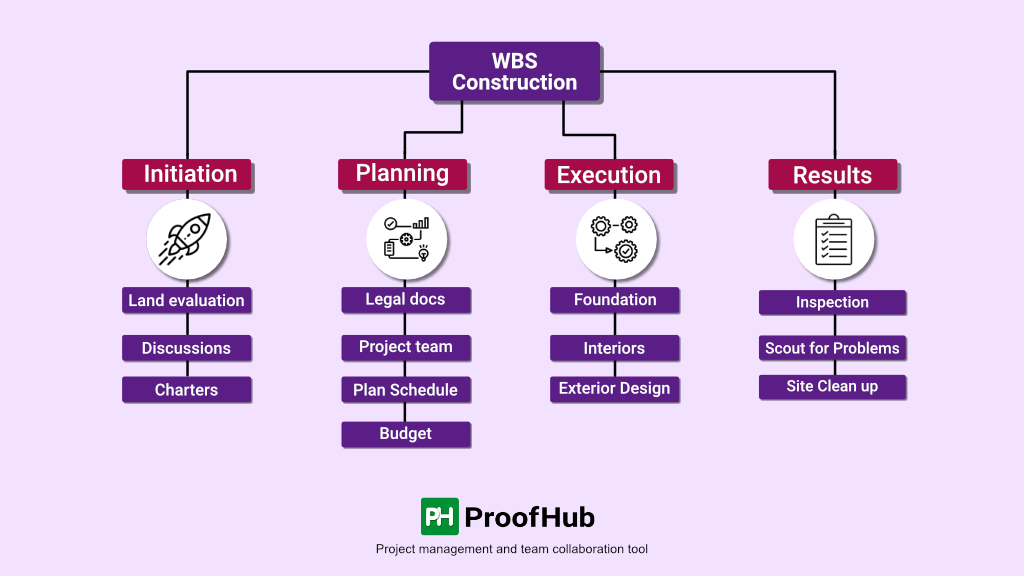
WBS in project management
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is a project management tool that organizes a project’s deliverables and tasks into a hierarchy. It provides a visual representation of all project deliverables, tasks, and subtasks, guaranteeing that nothing is neglected and making project management easy.
The importance of work breakdown structure lies in its ability to help everyone comprehend the scope of a project. It is divided into levels, each representing a complete description of the project deliverables.
WBS is an excellent solution for complex projects with numerous steps and jobs since it splits all deliverables into manageable sub-deliverables. You can allocate a budget and a time estimate for each deliverable using this method, and ensure that the estimates sum up to the entire budget.
Some important work breakdown project management rules & requirements
As you create a work breakdown structure, here are some rules;
- According to the 100% rule developed by Gregory T. Haugan, a WBS should include 100% of the work that has to be done to complete the deliverables, excluding any work that is particularly not defined in the scope of the project (unrelated work). Be specific, be thorough!
- Do not include any amount of work twice. This will violate the 100% rule and will result in miscalculations.
- Focus on deliverables rather than actions.
- The work package should take no less than eight hours of effort but no more than 80. In other words, if you report on your work every 30 days, a work package should take no more than a month to complete.
What are the different types of WBS?
In project management, there are three basic types of work breakdown structures.
1. A process-oriented WBS: generates a comprehensive project scope by defining the project’s work phases, functions, and steps to be followed to accomplish the project.
2. A deliverable-oriented WBS: identifies the project’s deliverables, such as physical items that contribute to the overall project aim, and shows how they are related.
3. A time-phased WBS: It divides long-term projects into major phases rather than steps, with full planning occurring only during the approaching project phase.
Why use a WBS in project management?
Before discussing why let’s know what is a work breakdown structure in project management.
It’s simple. The work breakdown structure in project management visually defines manageable chunks of a project that a team can understand, as each part of the work breakdown structure gives further detail.
The goal of WBS in project management is to make a large project manageable. It helps you to:
- Develop a schedule
- Determine the cost of the project
- Set dependencies
- Write a statement of work
- Assign responsibilities and clarify roles
- Track the progress of a project
Project managers and teams often use project work breakdown structures to identify potential risks in a given project. As the project is divided into branches, if any branch is not defined up to the mark, it represents a scope definition risk. Such risks should be reviewed as the project executes. As the work breakdown structure is integrated with an organizational breakdown structure, the project manager will be able to identify the communication points and develop a plan for the whole project. Also, in such cases as the falling behind of a project, referring to WBS will help quickly identify the major deliverables that will be affected by a late sub-deliverable.
Work breakdown structure vs project schedule vs project plan
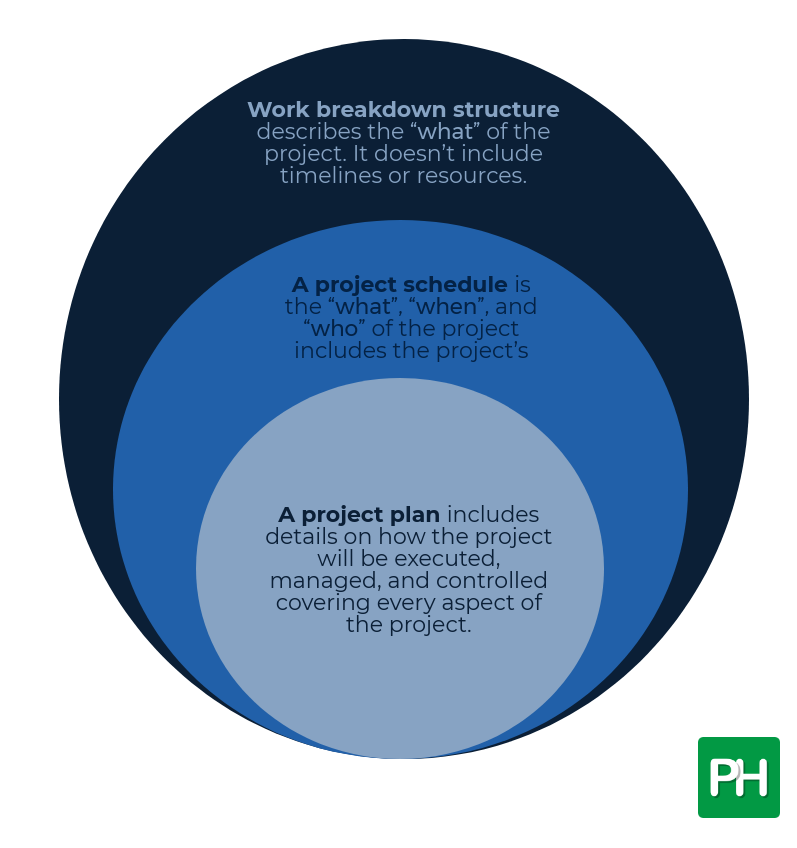
The difference between the work breakdown structure, project schedule, and project plan is a common confusion.
- Work breakdown structure describes the “what” of the project. It doesn’t include timelines or resources.
- A project schedule is the “what”, “when”, and “who” of the project includes the project’s deliverables as well as their deadlines and resource requirements.
- A project plan includes details on how the project will be executed, managed, and controlled, covering every aspect of the project.
The project plan is followed by the project schedule and then the work breakdown structure.
Some benefits of WBS in project management
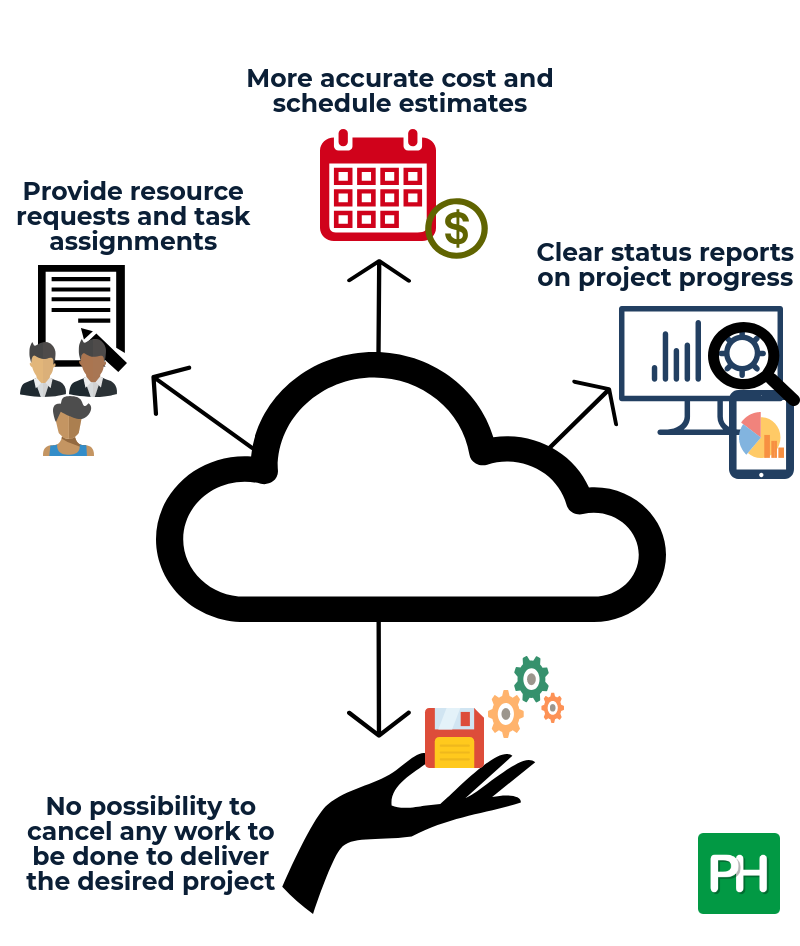
There are several benefits to developing a WBS for your project.
- All of the work to be done by the project is identified so you will be less likely to cancel any work to be done to deliver the desired results.
- It allows for a more accurate cost and schedule estimate.
- Provides a basis for resource requests and task assignments as you will be able to determine the skill sets needed to complete the work.
- Enable you to provide clear status reports on project progress.
Work breakdown structure (WBS) with ProofHub
Project teams can use tools like whiteboard, sticky note pad, or project management tools like ProofHub to identify major deliverables, sub-deliverables, and specific work progress. ProofHub is an easy-to-use online collaboration tool that supports work breakdown structures, project outlines, Gantt charts, and easy scheduling.
ProofHub has several tools that allow large and small project teams to have complete control over their assignments and projects. You can handle numerous parts of your work from a single location using these tools. ProofHub brings all of your team members together on a single platform, whether you’re leading an in-office or remote team. Collaboration becomes a lot easier and more natural as a result of this. Users can collaborate from anywhere with comprehensive collaboration features like online proofreading, group chat, task management, discussions, file management, and more, without having to travel back and forth in long email threads. It can help you create a comprehensive project breakdown structure, enabling clear visualization and organization of project tasks.
With ProofHub’s project management software app, you can plan all your project requirements in a streamlined way to make your project perfect. Use ProofHub to create consistent project performance, improve team productivity, increase project speed, hold the team accountable, and make sure no project slips through the cracks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a work breakdown structure (WBS) is a powerful project management tool that breaks down large projects into manageable chunks. It helps you dentify all the work required, estimate costs and timelines, and track progress more effectively. Are you looking to optimize your workflow and increase efficiency? try ProofHub today and see how a WBS can streamline your workload!
FAQs
How does WBS help teams with time management?
A project consists of various time-based tasks and assigned time frames and costs. By using a definite WBS team can manage time effectively, stay on top of deadlines, and never miss out on anything important. Its deliverable-oriented approach helps teams keep track of time devoted to everyday tasks and the overall time spent by each individual on a project.
What is the difference between WBS and CBS?
A Cost Breakdown System (CBS) is a phrase used in project management to describe a structure for estimating and tracking project expenses. A good CBS makes it easy to see how your project progresses about the schedule. CBS is closely associated with a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) represents all of the tasks completed within a project. The CBS represents all of the cost categories purchased within tasks.